What Do You Mean By Rudder Drop?
Rudders and related manoeuvring systems are as old as the ships themselves. They perform the very important task of manoeuvring the vessel as and when required. Rudders are based on the simple physics of balancing moments where the induced rudder action causes a moment that is countered by the reverse moment of the hull, leading to the change in the vessel’s heading.
Rudders are also of various types, and selecting a rudder is paramount to a designer at the initial stages of basic design for any vessel.
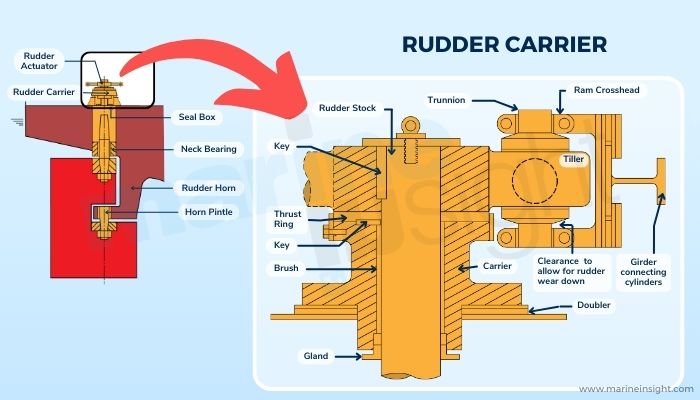
As we have learnt, the rudder is directly connected to the rudder stock, which is operated by the tiller system and that, in turn, is primed by the rest of the steering gear apparatus.
All connections between the respective parts of this entire mechanism are secured by a system of clamps, bearings, bolts, gaskets, and so on. Like all other mechanical systems, rudders are also subject to wear and tear due to constant use over the years of the vessel’s operation.
With time, all such joints and junctions gradually lose their intactness leading to loosened connections. One of the most critical points is the point of attachment between the rudder stock and the tiller through the rudder bearing. As the connection loosens, the entire rudder carriage, which is the rudder and the stock along with related parts, somewhat does down and becomes slacker.
For example, when you fit a new fan in your room, it is well secured to the ceiling. However, after your use, you may notice that it starts somewhat wobbling. This is owing to the loose connections that happen at the location of attachment of the fan as a result of wear and tear. This is not to be taken lightly, and at this point, you must contact an electrician to look into the matter or get a new fan.
Similarly, for rudders, any loose connection beyond certain limits requires attention. This indicates loosening or slackness at the contact point in the way of the rudder bearing that connects the rudder with the rest of the steering gear arrangement starting from the tiller mechanism, which acts as a prime mover turning the rudder blade from time to time.
If this goes unchecked, the rudder bearings get worn down further and pose a risk of coming off. For vessels underway a voyage, this is a very unwanted risk that needs to be mitigated without fail.
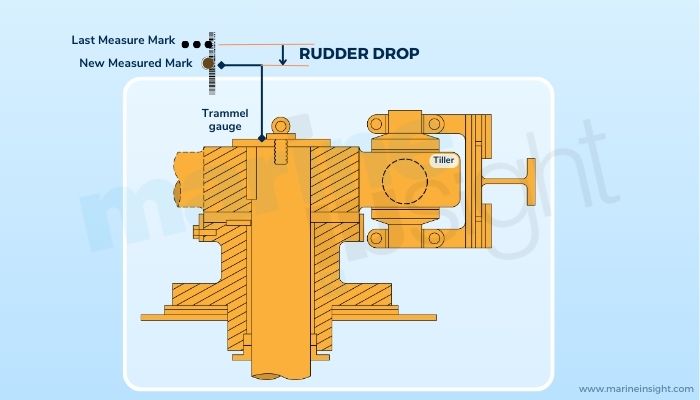
Rudder drop is a traditional indicator in checking the wearing down of a rudder over time. In physical terms, rudder drop is the distance the operational rudder arrangement has further travelled concerning a reference point on the hull.
As we know, for all practical purposes, rudders are attached to the rudder stock at the aft of a vessel underneath the stern area. The rudder stock, in turn, is operated by the tiller mechanism housed inside the steering gear arrangement space.
As mentioned, this point of contact between the rudder stock and the tiller through the bearing is very crucial. If there is a loose end at this point, it could be reflected as an increase in distance between the rudder stock and a reference point.
Now what is the reference point? The reference point is usually a fixed point inside the hull, like a structural member. The distance is essentially measured between this point and any point on the rudder stock.
Now, the distance is initially measured and kept on record during the vessel’s construction or launch stage. It is then periodically checked over the years. The difference in the distance measured initially and then at a later stage is called the rudder drop.
How is this distance measured?
For years, the trammel gauge has been a simple apparatus used. It is an L-shaped instrument with two legs at right angles such that one of the tips is on the rudder stock and another is on the fixed point. During the initial measurement, the points of contact of the gauge are marked by either punching a hole or making a drill.
Later when the clearance is measured again, if the position of the mark as gauged shifts from the initial readings, there is a clear rudder drop. These new readings are considered, and any significant difference is brought to attention.
You might also like to read-
- How Does A Rudder Help In Turning A Ship
- Types of Rudders Used For Ships
- Revolutionary Rudder Force Detection System for Dynamic Positioning Operation
- What Is Lowermost Deck In A Ship?
Disclaimer: The authors’ views expressed in this article do not necessarily reflect the views of Marine Insight. Data and charts, if used in the article, have been sourced from available information and have not been authenticated by any statutory authority. The author and Marine Insight do not claim it to be accurate nor accept any responsibility for the same. The views constitute only the opinions and do not constitute any guidelines or recommendations on any course of action to be followed by the reader
The article or images cannot be reproduced, copied, shared or used in any form without the permission of the author and Marine Insight.
Do you have info to share with us ? Suggest a correction
Latest Naval Arch Articles You Would Like:
Subscribe To Our Newsletters
By subscribing, you agree to our Privacy Policy and may receive occasional deal communications; you can unsubscribe anytime.
Web Stories

About Author
Subhodeep is a Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering graduate. Interested in the intricacies of marine structures and goal-based design aspects, he is dedicated to sharing and propagation of common technical knowledge within this sector, which, at this very moment, requires a turnabout to flourish back to its old glory.