SOLAS requirement for Global Maritime Distress Safety System (GMDSS)
Safety of life at sea is the highest concern in the shipping industry and therefore several norms and regulations have been laid down to meet the minimum level of safe operation and procedures to avoid any mishap. In spite of all the regulations, some accidents are hard to avoid. Thus, SOLAS clearly describes the minimum criteria for Global Maritime Distress Safety System (GMDSS) so during a mishaps or accidents, maximum number of lives can be saved.
All the ship traveling in international seas must comply with the SOLAS chapter IV for a smooth and clear operation of distress system all over the world. Thus, following functional requirements were laid down:
Transmission of distress signal from ship to shore by at least two separate and independent methods
Every ship under GMDSS must have at least two separate communication method for ship to shore distress transmission from the following- EPIRB, Digital Selective Calling (DSC), Inmarsat C.
Receiving of distress alert from shore to ship
Every ship under GMDSS must be capable of receiving shore to ship warnings and distress alerts by either of two means- DSC and NAVTEX.
Transmission and receiving of distress alerts in between ship to ship
Every ship under GMDSS must be capable of transmitting and receiving distress signal between ship to ship by two methods – VHF channel 13 and DSC.
Transmission and receiving of search and rescue coordinating communications
Every ship under GMDSS must be capable of receiving and transmitting search and rescue coordinating communications by any of the following means- NAVTEX, HF/MF/VHF, Inmarsat.
On scene communication transmission and receiving
Every ship under GMDSS must meet the requirements to co-ordinate search and rescue and other distress communication in between vessels at the scene of incident. Normally MF/HF or VHF is used.
Transmitting and receiving signals for locating
Ship under GMDSS must be fitted with proper approved equipment for maritime distress operation and as described in SOLAS chapter V like radar etc.
Transmission and receiving of maritime safety information
Every ship under GMDSS must be capable of receiving maritime safety information through services like navigation warnings, chart correction, weather forecast and warning, distress alerts etc by means of NAVTEX and DSC
General radio communication to be transmitted and received from shore based networks
Ship under GMDSS consist of a general communication system for official, business, personal and private crew communications and can be done by means of DSC and Inmarsat.
Transmission and receiving of communication between bridge to bridge
Ship under GMDSS must have a system to communicate bridge to bridge, which is normally done at port or pilot-age by means of VHF for normal range and MF/HF or Inmarsat for longer range.
You may also like to read-How Nautical Almanac Helps in Marine Navigation?
References:
IMO
Latest Ship Safety Articles You Would Like:
Do you have info to share with us ? Suggest a correction
Latest Maritime law Articles You Would Like:
Latest News
- What are Logistics Risks?
- How Port and Terminal Operators Can Control Emissions?
- Minimum Quantity Commitment (MQC) and Liquidated Damages in Container Shipping: Concept and Relevance
- The Essential Guide to Shipping Container Dimensions – What You Need to Know
- A Comprehensive Overview of IMDG Code for Shipping Dangerous Goods
- Nautical Law: What is UNCLOS?
Subscribe To Our Newsletters
By subscribing, you agree to our Privacy Policy and may receive occasional deal communications; you can unsubscribe anytime.
Web Stories





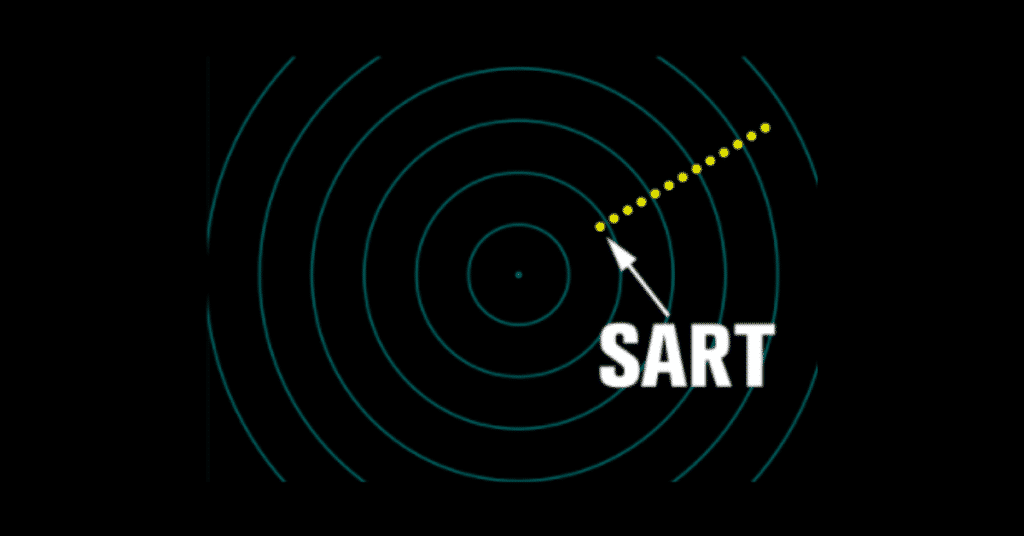




























Please be alert that it can be difficult to get hold of GMDSS spares. A good place to look is here:
Has DSC reception via the radar display been added , this would be the nmea DSC position information upon reception by a DSC radio on the bridge and the nmea message sent to the Arpa radar to show direction and position on the radar screen .