What is Garbage Management Plan (GMP) on a Ship?
Factors adding to Marine pollution comprise of not only the effects of oil and harmful gas emissions but also garbage generated on the ship during normal operation. Such garbage matter includes plastic, synthetics, oil rags, cardboard boxes etc., which are equally harmful for marine organisms and environment as is oil to the sea.
What is the Definition of “Garbage” on Ship?
Garbage on ship means all kind of victual domestic and operational waste excluding fish and parts thereof, food waste, generated during the normal operations of the ship and liable to be disposed of continuously or periodically except those substances which are listed in other Annexes of MARPOL convention.
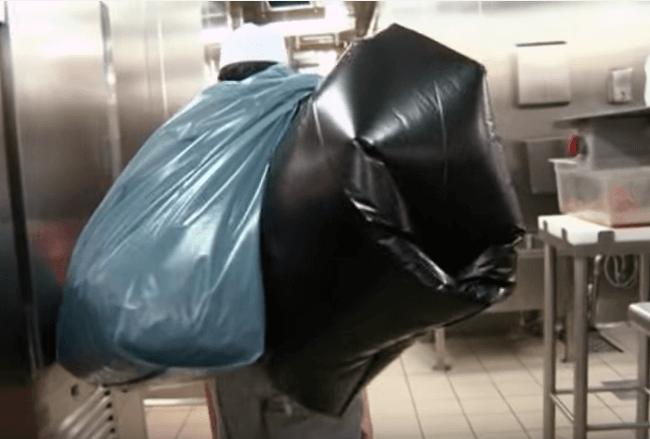

What is Garbage Management Plan (GMP)?
The Garbage Management Plan is a complete guideline which comprises of a written procedure for collecting, storing, processing, and disposing of garbage generated onboard ship as per regulations provided in Annex V of MARPOL.
Training must be given to ship’s staff for proper garbage disposal onboard ship and for knowledge on garbage disposal regulations at sea and in special areas.
Where is GMP Applicable?
A GMP is mandatory for all ships above 100GT and on ships certified to carry 15 persons or more and it is written in the working language of the crew as per the guidelines developed by the organisation.
GMP to be retained onboard as a record for a period of two years from the date of last entry.
A Responsible officer is to be in charge for maintaining garbage management plan on ship. Normally chief officer is responsible along with 2nd engineer (engine department).
Brief about GMP
An approved garbage management plan must consist of the following-
- Ships details.
- Overview of Annex V of MARPOL.
- List of equipments for handling garbage on ship.
- Placards to be posted for disposal criteria.
- Possible local recycling arrangements.
- Written procedures for Collecting Garbage.
- Garbage segregation description to avoid intermixing of garbage which includes Identification of suitable receptacles for collection & separation.
- Garbage processing methods available on the ship.
- Garbage storing methods and garbage station.
- Garbage disposal methods.
- Entry to be made in garbage record book.
- Emergency and accidental discharge criteria.
- Needs of the reception facilities.
- Identify the available operating & maintenance procedures of collecting equipment on board.
- Describe the training or education programs to facilitate the processing of garbage.
- Identify the location of each collection point.
You may also like to read-What is Marine Debris ? & What is Green Ship Recycling?
Do you have info to share with us ? Suggest a correction
Latest Maritime law Articles You Would Like:
Latest News
- What are Logistics Risks?
- How Port and Terminal Operators Can Control Emissions?
- Minimum Quantity Commitment (MQC) and Liquidated Damages in Container Shipping: Concept and Relevance
- The Essential Guide to Shipping Container Dimensions – What You Need to Know
- A Comprehensive Overview of IMDG Code for Shipping Dangerous Goods
- Nautical Law: What is UNCLOS?
Subscribe To Our Newsletters
By subscribing, you agree to our Privacy Policy and may receive occasional deal communications; you can unsubscribe anytime.
Web Stories



















Lots of people don’t harmonize it but 143,000 electronics are stored absent permanently a day.
This is the reason job opportunities are not only
created locally but also globally. Lots of issues are noticed in the process of disassembling of the electronic waste.
What is the limitation for Exhaust gas boiler washing water discharge ??
How to make a GMP of vessel ? Where it to be pasted On board
Special areas???
requirement is the carrying GMP 400GT and above.not 100 GT and above
@Dinuka: Please check this – https://www.imo.org/en/OurWork/Environment/PollutionPrevention/Garbage/Pages/Default.aspx
for 400GT and above, the ships needs to have a Garbage Record Book.