What are Passenger Ships?
It is an umbrella term which covers many aspects under itself, but in more or less general form passenger ships are the merchant ships generally employed for transportation of passengers or voyagers. So, these are the merchant ships which carries passengers on national or international voyages. They can be as small as yachts and as big as giant cruise ships.
Merchant vessels that are employed to aid in the transiting of voyagers and passengers through the medium of water transportation are referred to as passenger ships. The terminology, however, covers a lot of aspects under its umbrella, thus rendering a generalised nature to its nominal citation.
The criteria for passenger vessels are governed as per stipulations set by the International Maritime Organisation (IMO). These stipulations not only specify the minimum amount of surface area required for a dozen voyagers but also lay down the regulatory requirements to ensure the safety and security of passengers.
History Of Passenger Ships
Sailing is the oldest mode of transportation. Simple boats made up of tree hides were used to travel by sea. Scientists and researchers used ships for their explorations. Ships play a key role in the world’s economy. Advancement in these ships goes hand in hand with the development of mankind.
Traces were found of first known vessel, made up of animal skin or woven fabrics and belonged to Neolithic period, about 10000 years back. These vessels were not shipped in any regard but initiated transportation across water bodies. By 3000 B.C. Ancient, Mesopotamian and Egyptians were the first to make use of boats made up of wooden planks’ hull on large scale transportation across the Nile, Euphrates and Tigris.
Egyptians become proficient at making sailboats. 44m long Khufu Ship (built in 2500 B.C) revealed from the excavation in 1954 at Giza pyramid was a trademark to their skill. Later Greeks, Phoenicians and Romans also put their part in the development of modern ships.
Between 260 and 255 B.C, the first Roman Navy came into existence and developments were made in earlier developed ships. In the 5th century Germans developed fast moving oar-driven ships, their famous ship was 22m long Gokstad ship.
Between the 12th and 15th century, during the reign of the Song Dynasty “The Chinese Junk” (the boat which Marco Polo used for his explorations) was developed. It was the first time when such a bulkheaded strong boat was developed which can bear Chinese typhoons easily. These were large ships and made even more than 135m length.
In the 15th century, the Spanish carrack was the largest European sailing ship which becomes the standard vessel of Atlantic trade and adventure in the next century. There were some difficulties in sailing this ship because of unusually high castles in bow and stern.
Related Read: The History of Ships: Ancient Maritime World
In the 16th century, the English developed the ship galleon with a high stern and a relatively low bow. This was better than earlier. The galleon became the standard for all big ships. In 17th – 18th century various East India companies of England and Holland invest in magnificent ocean-going ships which were needed to have the capacity for a large amount of cargo, strong and well-armed. These were the most magnificent ships of that time. These were 50m long and 12 m wide and could not achieve a fast speed. These ships used trade winds as assistance in the journey. In 19th century speed of merchant ships became a factor and the age of clippers started.
Clippers were the passenger ships with relatively high sailing speed and consist of a square rig along with three or more masts. During the “Golden Rush” production and usage of clipper was on its peak, because in the transportation of gold from one region to other clippers were extensively used. With the introduction of steamships, the demand for high-speed clippers started declining. This is due to the reason that the steamships can sail in all sort of weathers. Later in the 20th century, construction of ships was triggered with the application of metal in ship construction. These metaled ships can bear harsh weather more efficiently and their further advancement results in present-day ships.
As per the classification of the classification society DNV (Det Norske Veritas), passenger’s vessels are also sub-divided into broad categories on the basis of their utilisation and size.
- Passenger ships that are utilised only for the purposes of transiting voyagers
- Vessels that in addition to transiting voyagers are also utilised to transit vehicles from one destination to another.
- Passenger vessels that also carry cargo
Categorisation Of Passenger Ships
The passenger ships are broadly categorised in two classes namely: Ferry and Cruise Ships.
Apart from this distinction, there have been specified numerous types of passenger ships. Each of the vessel types can be elaborated as follows:
Ferry Ships
Ferry ships are those vessels which are used to transit voyagers on short-natured water travel routes. Ferry ships can be dual in nature that is, either they can be vessels are only used for the purposes of transporting passengers or they can be ships that can also carry the vehicular load along with the intake of voyagers.
These ships go for their voyage on a regular schedule and have fixed fares.
Ferries are also referred to as water taxis or water buses. These are the ships which sail on the same route with many intermittent stops. These ships serve the same purpose as the public transport on road or rail do. So, ferries are the smaller ships used for smaller distance voyages or rather as public transport.
The transportation cost through ferries is much lowered as compared to bridges and tunnels. In some regions, ferries provide long distance services, Mediterranean Sea ferry service is the best example of long route ferry service. Ferry ships that are used for transporting not only passengers but also the vehicular loads, and loading and unloading to the ship is carried out through Roll-off/ Roll on systems are termed as Ro-Ro ferries.
India’s first ro-ro ferry, under Sagar Mala Project, runs between Ghogha and Dahej and started working on 22 October 2017. It connects South Gujrat and Saurashtra through only 31 km ferry run. A special type of ferry, which is used to carry passengers only, and sails on speed higher than conventional ferries is referred to High-speed ferry.
Ferry ships are those vessels which are used to transit voyagers on short-natured water travel routes. Ferry ships can be dual in nature that is, either they can be vessels are only used for the purposes of transporting passengers or they can be ships that can also carry the vehicular load along with the intake of voyagers.
The latter kind of ferrying vessels is referred to as a Ro/Ro vessels as they make use of ‘Roll On/Roll Off’ ramping systems to enable easy loading and unloading of the vehicles.
Read more about different types of ferries
Stena Hollandica – The Biggest Ferry in the World
High-Speed Ferries are a special type of ferries with the capability of sailing at high speed and are mainly used for transiting passengers.
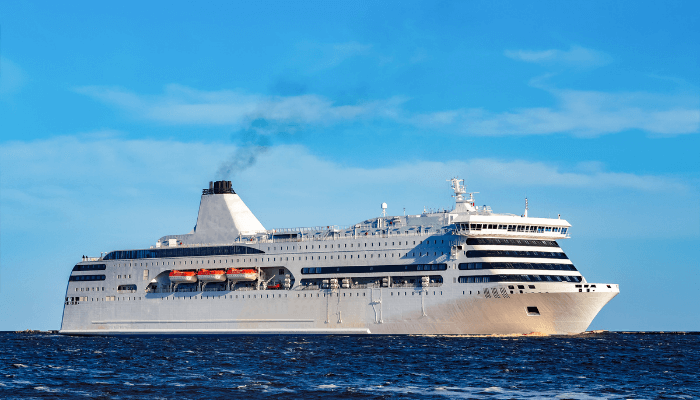
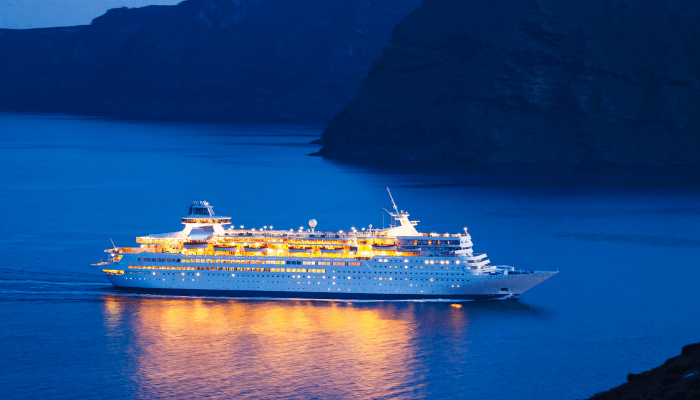
Cruise Ships
Large vessels equipped with all luxury and necessary amenities, used for transportation and destination vacations are referred to as Cruise Ships or generally cruises. These vessels are opted for long distance travel and bring the opportunity of international trade to the country.
The cruise ship offers a vacation full of fun and amusement. It provides a new and totally different vacation spot with a new experience for the vacationers. Being totally different from the usual vacation, a cruise offers swimming, jogging.
Cruise ships are the most famous type of merchant’s vessels which are used for transiting of passengers from one country to another for recreational trips.
These ships are also used for recreational activities, a media of social gathering and for country tourism due to availability of in-house guides and experts facility. Only design and amenities are not the thing, safety should be a major concern. Cruise vacations and cruise transportation are more favoured than other modes due to less cost and safer, calm, pleasant and pollution free environment.
Cruise ships are further subdivided on the basis of size into:
- Large cruise ships: Large cruise ships are the ships with larger voyager carrying capacities.
- Small Cruise ships: Small cruise are the ships with smaller voyager carrying capacities.
- Liners: These are the special sort of large cruises, equipped with best facilities. These look more or less like floating cities.
- Special Cruise ships: These are the ships which are designed for a special destination. For example cruise ships for visiting Antarctica region.
Though presently cruise vessels are used for recreational transiting of passengers, these vessels were preceded by voyager vessels that aided in the transporting of voyagers for commercial purposes internationally.
Since passenger vessels’ capacitance is quantified on the basis of their GRT (Gross Registered Tonnage), vessels which have been built with higher GRTs can be called as large cruise ships, while those with smaller GRTs can be denoted as small cruise ships. The voyager carrying capacitance would also likewise vary between the likes of the larger and smaller cruise ship types.
These days, passenger’s vessels are like floating cities, having the very best luxuries and facilities for a safe and lavish voyage. Read more about the top luxury cruise ships in the world. Moreover, some of the biggest and best ships in the world are cruise ships.
Read about some amazing cruise ships:
10 Largest Cruise Ships in the World
Allure of the Seas & Oasis of the Seas – The Largest Cruise Ships in the World
Liners are a more traditional form of cruise ships which are used to transit passengers from one country to another, along with the best amenities.
Special Cruise Ships
Cruise ships built for visiting specific regions of the world are termed as special cruise ships. For e.g. cruise ships visiting Polar Regions (Arctic and Antarctic) are called polar cruise ships. They are specially designed and built to face the tough environment of such extreme climatic regions.
Passenger ships, both of the ferry ships and the cruise ships variances, have become extremely popular in contemporary times. Providing a sense of novelty amongst the likes of road, rail and aerial travelling options, passenger’s vessels help people to re-associate themselves with the marvel that only oceanic vistas can offer.
Market Statistics Of Passenger Ships
The interest of people travelling in cruises and passenger ships have shown a great rise, hence increasing the potential of the international passenger ship’s market. There has been an increase of more than 1.1 million passengers travelled via water ways. The Cruise Line International Association (CLIA) predicts that over 28.5 million People will be using waterways as the means of transport during the year 2019-2020.
Most of the passengers using the cruise /passenger ships hail from the United States, therefore the highest cruise capacity is allocated to the Caribbean, whereas the Mediterranean is the second most popular destination in the international market and non-European destinations hold the third position.
Future Of Passenger Ships
The passenger ships and their variations are in a constant state of evolution with the competition remaining fierce between the operators and owners. In this competitive era of globalisation, the following trends are observed.
- Increasing embarkations from “close-to-home” ports
- Greater focus on family and family travel
- Increase in river cruises
- Exotic locales and itineraries
- Growing Variety of Ships
- Growth in Drive Market Cruises
- The boom in Theme Cruises
- New destinations
These upcoming trends will not only fuel up the international market with lots of new ideas and innovation. But will also be very good for the upcoming future of the shipping industry.
Passenger ships have always played a vital role in the global shipping market and will always be.
You may also like to read – Titanic vs Modern Cruise Ship: How Ships Have Evolved
Disclaimer: The authors’ views expressed in this article do not necessarily reflect the views of Marine Insight. Data and charts, if used, in the article have been sourced from available information and have not been authenticated by any statutory authority. The author and Marine Insight do not claim it to be accurate nor accept any responsibility for the same. The views constitute only the opinions and do not constitute any guidelines or recommendation on any course of action to be followed by the reader.
The article or images cannot be reproduced, copied, shared or used in any form without the permission of the author and Marine Insight.
Do you have info to share with us ? Suggest a correction
Subscribe To Our Newsletters
By subscribing, you agree to our Privacy Policy and may receive occasional deal communications; you can unsubscribe anytime.
Web Stories